Most Common RabbitMQ Use Cases
Scalegrid
AUGUST 27, 2024
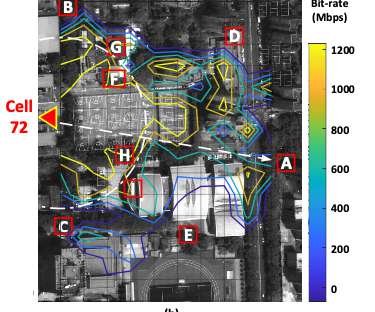
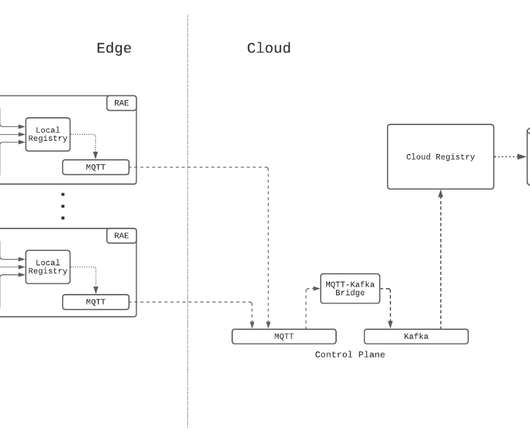
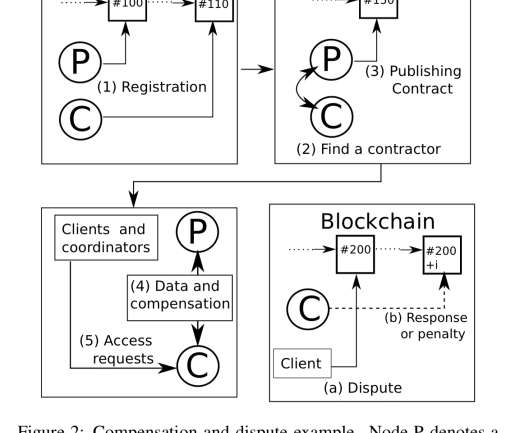
Wondering where RabbitMQ fits into your architecture? This article expands on the most commonly used RabbitMQ use cases, from microservices to real-time notifications and IoT. RabbitMQ excels at managing asynchronous processing and reducing latency while distributing workloads effectively across the system.



























Let's personalize your content